Big Data

Big Data has been buzzing around for quite some time, but there are a lot of misconceptions surrounding it. In this post, I would try my best to explain Big Data in the simplest way I can.
Big Data refers to a huge volume of data, that cannot be stored and processed using the traditional computing approach within a given time frame.
But how huge this data needs to be? To be termed as Big Data?
There is a lot of misconception surrounding, what amount of data can be termed as Big Data. Usually, the data which is either in gigabytes, terabytes, petabytes, exabytes or anything larger than this in size is considered as Big Data. This is where the misconception arises. Even a small amount of data can be referred to as Big Data depending on the context it is being used. To get more clarity on this let me make use of a few examples and explain it to you.
For example, if we try to attach a document that is of 100 megabytes in size to an email we would not be able to do so. As the email system would not support an attachment of this size.
How Big Data is Classified?
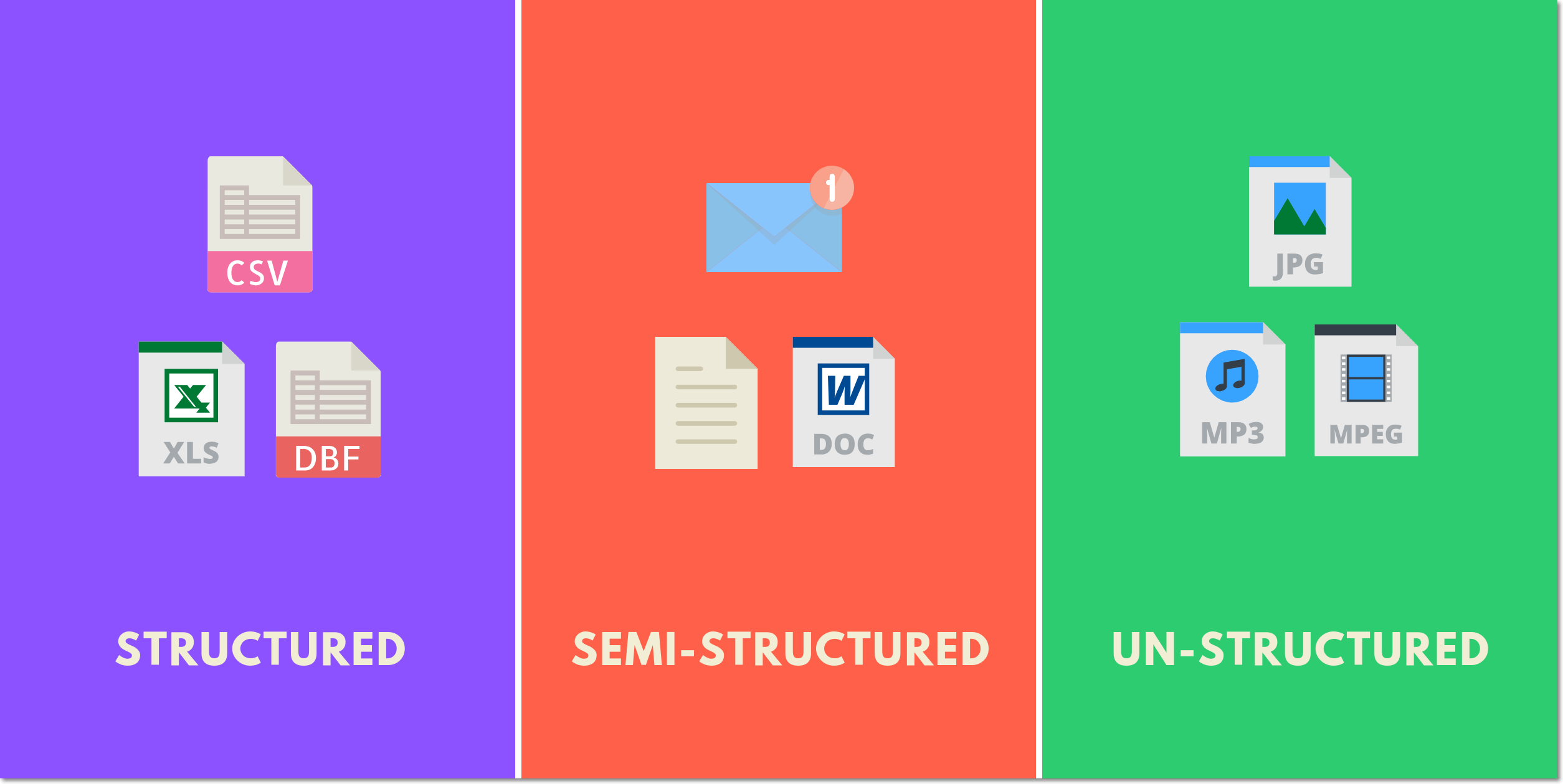
Big Data is classified into 3 different categories.
1. Structured Data
2. Semi-Structured Data
3. Unstructured Data
Structured Data refers to the data that has a proper structure associated with it. For example, the data that is present within the databases, the CSV files, and the excel spreadsheets can be referred to as Structured Data.
Semi-Structured Data refers to the data that does not have a proper structure associated with it. For example, the data that is present within the emails, the log files, and the word documents can be referred to as Semi-Structured Data.
Un-Structured Datarefers to the data that does not have any structure associated with it at all. For example, the image files, the audio files, and the video files can be referred to as Un-Structured Data.